The SG of fiber reinforced composites can be represented as shown below.
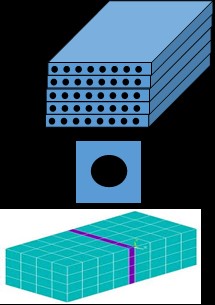
Let the material properties of the fiber and matrix be:
Fiber: E11 =230 GPa, E22 =15 GPa, G12=G13 =15GPa, G23 =7GPa, v12=v13 =0.2000
ν23 =0.0714.
Matrix: E =4.0GP, ν=0.35
Fiber volume of fraction is assumed to be 60%
The material properties are obtained from:
“Soden, P. D., Hinton M. J. and Kaddour, A. S., Lamina properties, lay-up configurations and loading conditions for a range of fibre reinforced composite laminates. Compos. Sci. Technol., 1998, 58(7), 1011”
youtube link.
https://youtu.be/Bf-uKbd57uw
Step 1: Input material properties
There are two materials namely fiber and matrix
Step 2: Select appropriate SG
a. Select 2D SG that represent the current example
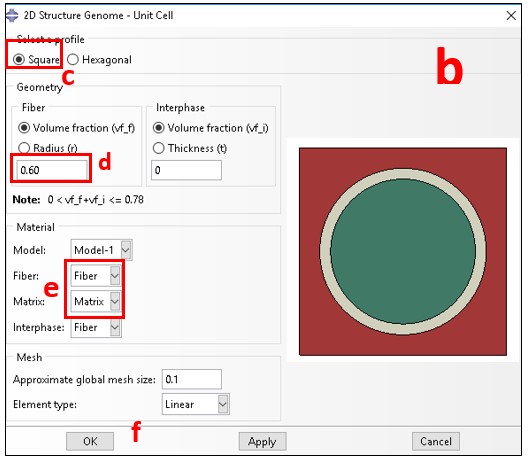
b. 2D SG wizard shows up
c. Select Square pack as microstructure
d. Add fiber volume fraction
e. Select material properties for fiber and matrix
f. Click on OK to generate the SG
g. See generated 2D SG
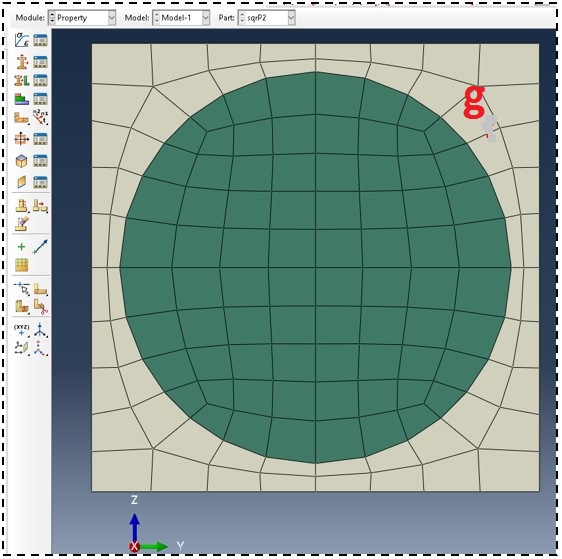
Step 3- Homogenization- 3D effective properties
a. Click on Homogenization
b. Homogenization wizard shows up ( see below)
c. Select 3D (solid) Model
d. Select analysis type, elastic
e. Click on OK to start homogenization
f. See the predicted 3D effective properties
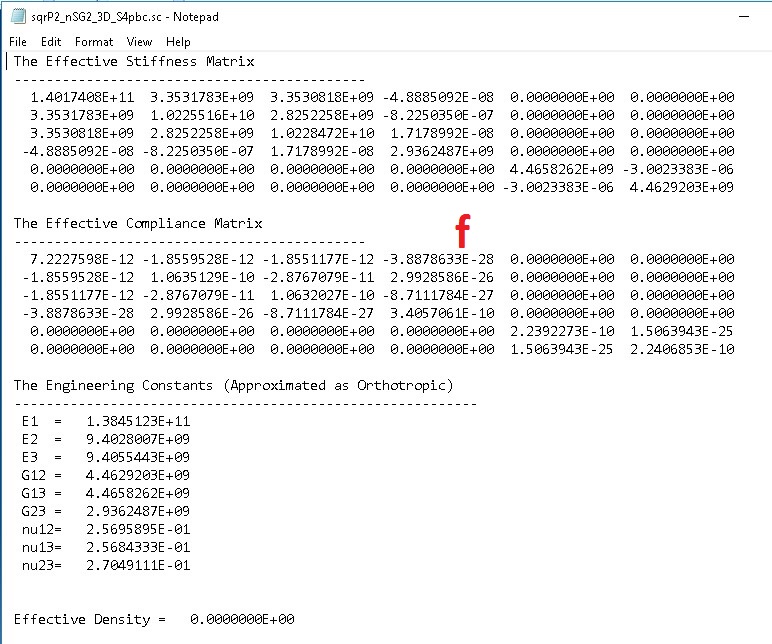
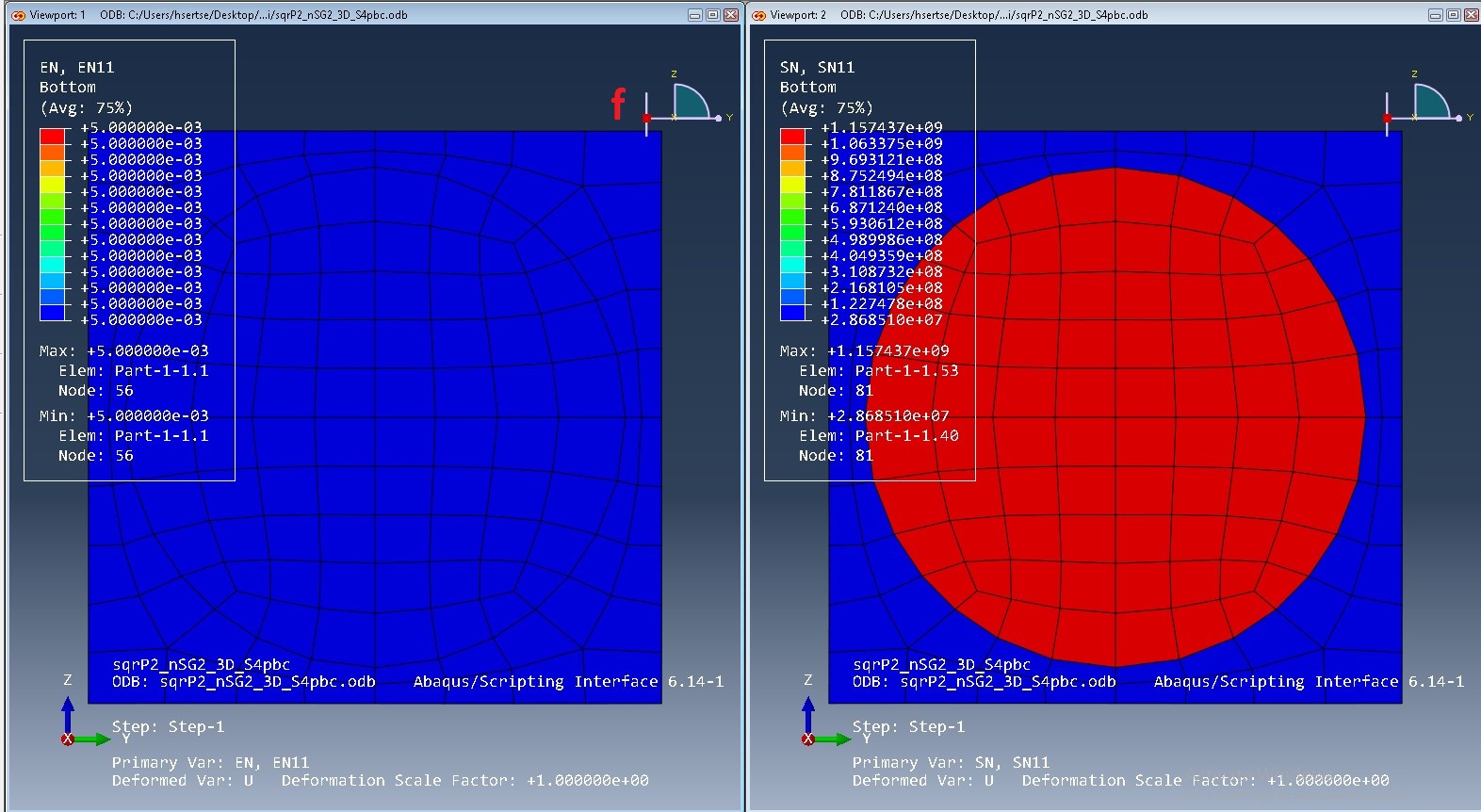
Step 4: Perform dehomogenization
a. Select dehomogenzation
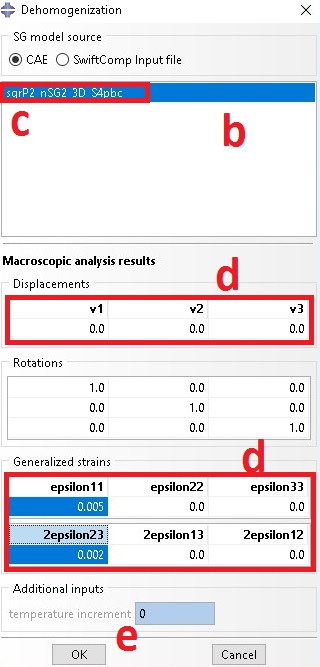
b. Dehomogenization wizard shows up
c. Select opt file
d. Add displacement to recovery displacement or strain loading to recover both local strain and stress, for current example problem let e11 be 0.005 and 2e23 be 0.002
e. Click on OK to start dehomogenization
f. See, dehomogenization
youtube link.
https://youtu.be/Bf-uKbd57uw